Tracking SKU performance is essential for improving profits, managing inventory, and meeting customer demand. By focusing on key metrics, businesses can identify top-performing products, reduce costs, and make smarter decisions. Here are the main takeaways:
- SKU Turnover Rate: Measures how quickly products sell and are restocked. Aim for a ratio between 5 and 10.
- Gross Profitability per SKU: Tracks profit margins after accounting for all costs. Margins above 40% are strong, while below 20% may need attention.
- Stock Levels and Holding Costs: Helps balance inventory to avoid overstocking or stockouts, with holding costs typically 20%-30% of inventory value.
- Sales Volume per SKU: Shows demand trends and guides marketing or reordering strategies.
- Dead Stock Identification: Identifies unsold inventory (90-180 days) to free up capital and space.
Advanced metrics like demand forecast accuracy, anomaly detection, and service levels provide deeper insights for long-term planning. Tools like AI-powered platforms handle large datasets, improve forecasting, and automate inventory management, saving time and reducing costs.
Focusing on these metrics ensures better inventory control, optimised stock levels, and improved profitability.
Why Tracking Sales by SKU is Crucial for Amazon Sellers | Learn from 417k+ Amazon Seller Reviews
Core SKU Performance Metrics to Track
As mentioned earlier, having accurate data is critical. To manage SKUs effectively, there are five key metrics you need to monitor. Each one provides valuable insights that can guide your inventory decisions.
SKU Turnover Rate
The SKU turnover rate measures how quickly products sell and are restocked. It’s calculated by dividing the cost of goods sold (COGS) by the average inventory. This metric helps you understand whether your products are moving efficiently or sitting unsold.
A high turnover rate reflects strong sales and efficient inventory management. On the flip side, a low turnover rate may point to overstocking, weak sales, or outdated inventory. Many businesses aim for a turnover ratio between 5 and 10, which means inventory is sold and replenished every one to two months.
"Inventory turnover is typically measured either at the SKU (Stock-Keeping Unit) level, or averaged out at a more aggregate level."
– Joannes Vermorel, March 2020
Turnover rates also vary by industry. For example, high-volume, low-margin sectors tend to have higher turnover, while low-volume, high-margin industries usually see lower ratios. If you’re dealing with low turnover SKUs, consider strategies like adjusting prices or bundling products. Tracking turnover at the individual SKU level gives you better control and helps you refine pricing and supply chain decisions.
Gross Profitability per SKU
To identify which products contribute most to your profitability, you need to calculate gross profitability at the SKU level. This involves accounting for all costs, including COGS, selling fees, shipping, and advertising, rather than just looking at revenue.
Gross profitability is calculated by subtracting these costs from sales revenue. A profit margin above 40% signals strong performance, while anything below 20% may require attention. Using the FIFO (First-In, First-Out) method can help track cost changes over time. Additionally, analysing the SKU ratio (percentage of SKUs in each profit range) and the sales ratio (units sold in each profit range as a percentage of total sales) can highlight underperforming products that might be hurting your bottom line.
Stock Levels and Holding Costs
Monitoring stock levels and their holding costs is crucial for avoiding the risks of overstocking or running out of inventory. Metrics like days of inventory on hand - how long your current stock will last at current sales rates - are invaluable for planning reorders.
Holding costs, which can account for 20% to 30% of your capital, include expenses like warehouse rent, insurance, staff wages, depreciation, and fulfilment fees. Keeping a close eye on these costs allows you to set appropriate reorder points and adjust safety stock levels based on demand and lead times. This ensures you’re not tying up unnecessary capital in inventory.
Sales Volume per SKU
Tracking the number of units sold for each SKU over time provides insight into demand patterns, seasonal trends, and the impact of promotions. This metric helps you allocate marketing resources and make informed reordering decisions.
By pairing sales volume data with profit margins, you can identify which products are most valuable. For instance, a high-volume, low-margin product might be essential for cash flow, while a low-volume, high-margin product could yield greater profit per unit. Sales volume trends can also guide marketing strategies, whether it’s boosting advertising for fast-growing products or supporting slower-moving ones with promotions.
Dead Stock Identification
Dead stock - inventory that hasn’t sold in a significant period - can account for 20% to 30% of total inventory. These items drain profitability by tying up capital, increasing carrying costs, and occupying valuable warehouse space. Identifying and addressing dead stock quickly is essential.
"Dead stock can be a major expense that reduces profitability by stalling revenue, increasing carrying costs and taking up valuable warehouse space."
– Abby Jenkins, Product Marketing Manager
Products that haven’t sold in 90 to 180 days are often considered dead stock, though this timeframe varies by industry. Inventory management software can help track product movement and flag slow-moving items before they become a larger issue. Once identified, act quickly - options include discounts, bundling, alternative sales channels, supplier returns, or donations.
Regular audits for dead stock should be part of your inventory management routine. The sooner you act, the less impact these items will have on your profitability and cash flow.
Advanced Metrics for SKU Management
Effective inventory management goes beyond the basics. To truly optimise stock and meet business goals, it’s essential to track advanced metrics. These indicators provide a deeper understanding of SKU performance and help refine strategies for managing inventory.
Demand Forecast Accuracy
Predicting future demand is just as important as monitoring current performance. Demand forecast accuracy measures how closely your predicted sales match actual results, and it plays a critical role in inventory planning, production schedules, and resource allocation. Accurate forecasts help avoid stockouts and reduce excess inventory, creating a smoother operation overall.
Studies indicate that even a modest 1% improvement in forecast accuracy can cut inventory costs by 1.5% and boost service levels by 2%. While no forecast can be perfect, certain models perform better than others. For instance, a benchmark accuracy of 70% is considered solid for products with unpredictable demand or frequent promotions. However, what constitutes "good" accuracy depends on your industry and product specifics. Identifying consistent forecasting errors is key to improving your models.
Take Nestlé, for example. By reducing forecast errors by 40%, the company achieved a 2% increase in perfect order fulfilment and cut inventory levels by 5%.
To enhance your forecasting accuracy, factor in seasonal trends, holidays, and potential disruptions like supply chain issues. Regularly updating forecasts with fresh data and encouraging collaboration between departments ensures predictions stay relevant and actionable.
Anomaly Detection
Anomaly detection is all about spotting data patterns that don’t fit the norm. These irregularities could signal market changes, successful promotions, data entry mistakes, or external disruptions. Quickly identifying outliers allows you to refine forecasts, address risks, and make smarter inventory decisions.
Automated systems for anomaly detection are particularly useful, reducing the need for time-consuming manual reviews.
In practice, anomaly detection has proven valuable in various scenarios. For example, an e-commerce platform noticed a sudden sales spike in a product category. Analysis revealed the surge was driven by a viral social media campaign, enabling the company to adjust its inventory and marketing strategies. In another instance, a manufacturing firm identified a sharp sales drop for a specific product. Anomaly detection traced the issue to a supply chain disruption, allowing the company to address the problem and normalise operations.
To get started with anomaly detection, define clear goals - whether it’s improving forecasts or identifying fraud. Use historical and seasonal sales data, ensuring it’s clean and ready for analysis. Train your detection model with past data and keep refining it as new trends emerge.
Service Level per SKU
Service levels are a direct measure of how well you’re meeting customer demand. This metric complements turnover and stock level data by focusing on the likelihood of avoiding stockouts for each SKU. It’s a balancing act: keeping enough stock to satisfy demand while avoiding the high costs of overstocking.
Service levels typically range from 70% to 99%. A level below 70% might indicate poor customer service, whereas aiming for 100% is often unrealistic and can inflate inventory costs. The ideal service level varies based on factors like inventory expenses, the impact of stockouts, lead times, and your market position.
For instance, a company targeting a 99% service level based on product availability discovered that its actual order line fill rate was closer to 91% when measured across orders.
To set the right service level for each SKU, start by evaluating your current performance. Adjust targets based on lead times - higher targets for items with longer lead times and lower ones for quicker-to-replenish products. Collaborate with finance and sales teams to weigh the costs of stockouts against inventory expenses. You might also consider setting different service levels for products based on their revenue or profit margins.
Higher service levels usually require more safety stock, so it’s important to find a balance that aligns with your business goals. Inventory management software can help by calculating trade-offs and suggesting service levels tailored to your needs.
sbb-itb-499c055
Using AI Tools for SKU Performance Management
Managing SKU performance across a large number of SKUs can quickly spiral into a logistical headache without the right tools. Traditional spreadsheets just can't keep up with the complexities of modern e-commerce. This is where AI-powered platforms step in, shifting inventory management from a reactive chore to a proactive, predictive system that drives smarter decisions. It's a game-changer for businesses looking to stay ahead in SKU tracking.
How AI Improves SKU Tracking
AI takes SKU management to the next level by processing massive amounts of data in real time, achieving stock accuracy rates of 95–99%, compared to just 63% with older methods. For example, a fast-fashion brand used AI to analyse historical sales data alongside factors like weather and marketing campaigns, which boosted their forecast accuracy by 34%.
AI also helps prevent inventory mishaps through automated alerts and threshold management. Its dynamic demand forecasting considers seasonal trends, promotional activities, market shifts, and external influences. Take the case of a grocery chain operating in both metropolitan and Tier 2 cities: by leveraging AI, they optimised stock distribution. This led to a 23% reduction in excess inventory of perishable goods in low-demand areas, while ensuring high-demand zones remained well-stocked.
The financial benefits are hard to ignore. Companies that adopt AI-driven inventory systems often see up to a 30% cut in carrying costs, a 15% drop in inventory levels, and 20% fewer stockouts. For businesses losing up to 11% annually due to inefficient inventory practices, these improvements directly boost profitability. With such compelling results, it's no surprise that AI-powered solutions are becoming indispensable.
Forthcast's Role in SKU Management
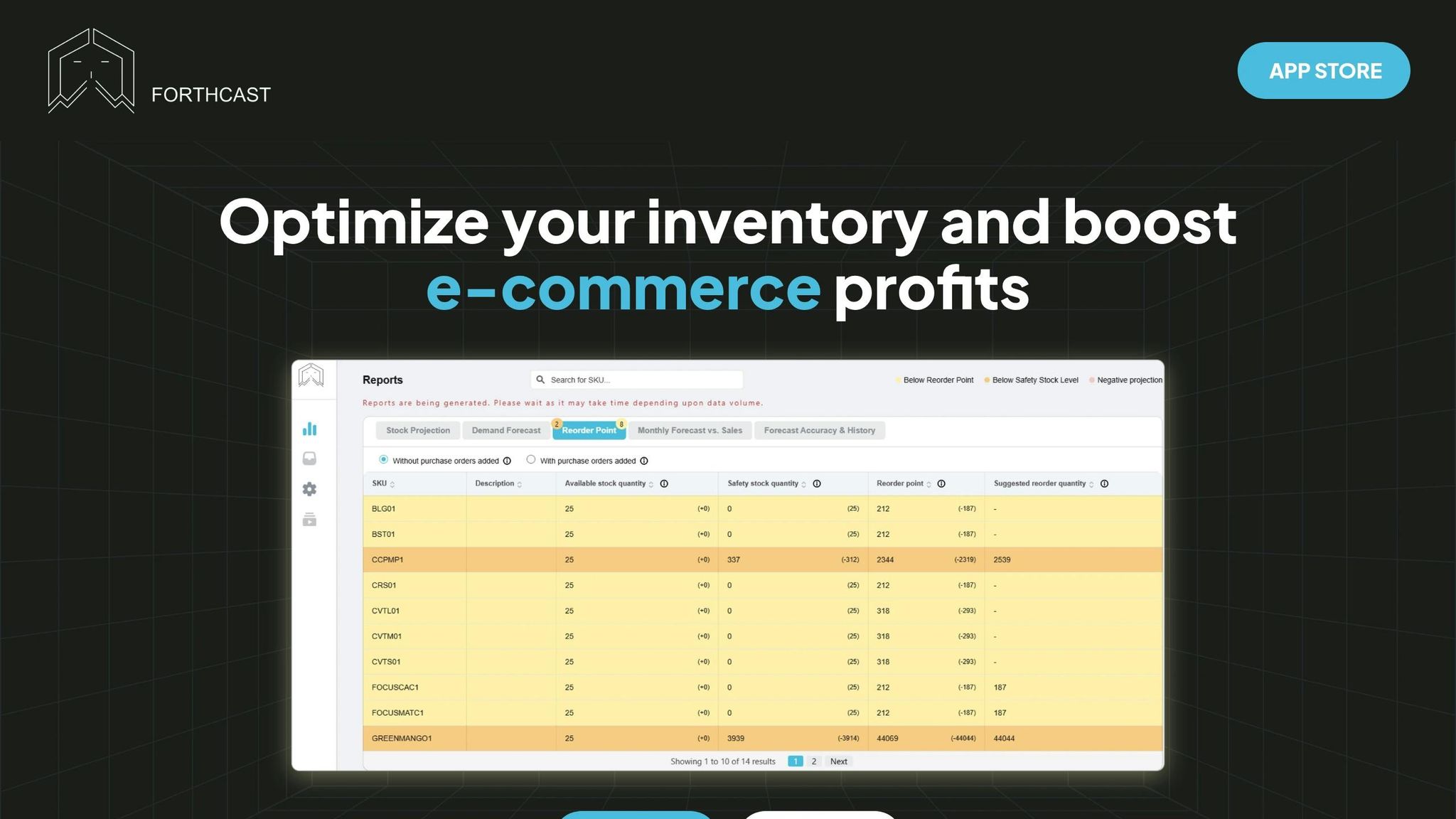
Forthcast builds on AI's proven strengths, addressing the unique challenges of SKU tracking in the e-commerce space. The platform blends advanced forecasting with practical tools tailored for online retailers.
With six-month demand projections, Forthcast gives businesses the foresight they need for effective planning. Instead of scrambling to fix stock issues as they happen, companies can anticipate demand trends and align their procurement schedules. The system even factors in lead times for each item, ensuring reorder suggestions are realistic and in sync with supplier timelines.
One standout feature is Forthcast's SKU-level anomaly detection. This tool flags unusual sales patterns, which could point to new market opportunities, supply chain hiccups, or data inconsistencies. For instance, Zara used AI-driven inventory management to cut inventory levels by 10% while increasing sales by 5%.
The platform's smart reorder suggestions take the guesswork out of replenishing stock. By analysing current inventory, projected demand, and lead times, it recommends optimal reorder quantities and timing. Additionally, its bundle management feature identifies relationships between products, automatically adjusting individual SKU forecasts when items are frequently bought together.
Forthcast also allows businesses to enrich forecasts with factors like promotions, seasonal trends, and market insights. Its accuracy tracking tools measure bias and error rates, providing continuous feedback to fine-tune inventory strategies over time.
Practical Checklist for Monitoring SKU Performance
Keeping a close eye on SKU performance requires a structured approach. By setting up clear processes, you can uncover trends and make informed decisions without unnecessary guesswork.
Key Metrics to Review Regularly
Regularly reviewing key metrics can help you avoid costly mistakes. Weekly check-ins are great for addressing immediate concerns like stock levels or unusual activity, while monthly reviews provide the chance to dig deeper into trends like profitability, turnover rates, and seasonal patterns.
Pay attention to sales volume alongside gross profit margins. A product might sell in high volumes but generate minimal profit, whereas a slower-moving SKU could be far more lucrative. A healthy turnover rate typically falls between 8 and 12. Anything below 4 could signal the risk of dead stock.
Stock levels are another critical area to monitor. Keeping an eye on current inventory and projected demand helps you anticipate stockouts, especially for seasonal items where timing is everything.
To make these insights actionable, use structured comparisons.
Using Tables for SKU Comparison
Tables are an excellent way to compare SKU metrics at a glance. They allow you to consolidate key data - like sales volume, turnover rates, gross margins, and stock days - into one place for easy analysis.
| SKU Code | Sales Volume (Units) | Turnover Rate | Gross Margin (%) | Stock Days | Performance Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SKU-001 | 1,250 | 8.2 | 32% | 28 | High |
| SKU-002 | 890 | 6.1 | 28% | 35 | Medium |
| SKU-003 | 320 | 2.8 | 15% | 67 | Low |
This format lets you quickly spot relationships between metrics. For instance, a product with high sales but low margins might need a price adjustment. On the other hand, a low-volume, high-margin item could benefit from extra marketing.
You can also segment comparisons by product category, price range, or seasonality for more targeted insights. Updating these tables monthly ensures you stay on top of performance shifts and can identify SKUs that demand further attention.
Setting Alerts and Thresholds
To turn insights into action, set up automated alerts and thresholds. For stock levels, base your thresholds on factors like lead times and demand variability. For example, if a product sells 50 units per week and has a 14-day lead time, setting reorder alerts between 150 and 200 units ensures you maintain a buffer.
Performance thresholds should align with your business goals and industry norms. For instance, flag inventory turnover below 4 times annually, gross margins that dip below acceptable levels, or significant drops in sales volume. These alerts can prompt timely reviews and adjustments.
You can also configure alerts for unusual demand changes, such as a 150% spike or a drop below 50%, to catch potential issues early. Similarly, margin alerts can signal when it’s time to revisit pricing strategies or supplier agreements.
Tools like Forthcast’s automated alert system simplify this process. By continuously monitoring inventory thresholds and providing smart reorder suggestions based on projected demand and lead times, such tools let you focus on big-picture strategies instead of getting bogged down by data.
Finally, adjust the frequency of alerts based on how volatile a product is. High-demand or seasonal items may need closer monitoring, while stable products might require fewer updates.
Conclusion
Keeping track of SKUs is a cornerstone of success in e-commerce. By monitoring key factors like turnover, profitability, stock levels, and sales velocity, businesses can make smarter decisions about pricing, inventory, and product strategies. This focused approach ensures resources are used effectively.
Analysing SKUs regularly can reveal ways to bundle products, potentially increasing the average order value by 20–30%, while also helping with seasonal planning that could boost sales by up to 30%. Machine learning takes this a step further, improving forecasting accuracy by as much as 20%.
AI tools are now essential for precise SKU management. Platforms like Forthcast provide valuable features, such as six-month demand forecasts, SKU-level insights, anomaly detection, and automated reorder notifications. These tools help maintain optimal stock levels, cutting down on carrying costs and removing the guesswork from reorder planning.
Key Takeaways
For e-commerce, SKU tracking should be an ongoing, strategic effort. Focus on key metrics like turnover, gross margin ROI, and sales velocity. Use methods like ABC analysis to rank products by their performance, and perform regular audits to pinpoint underperforming SKUs. Be ready to phase out those that consistently underperform. As mentioned earlier, regular reviews and automated alerts play a big role in keeping SKUs on track.
Set up automated monitoring systems and critical alerts to avoid the risks of stockouts or overstocking. Concentrate on metrics that lead to actionable insights.
"Don't go crazy with your SKU count. Focus on keeping a catalogue small whilst still being able to increase lifetime value and new sales. For a lot of brands, 3 SKUs make up 50% of sales. You probably don't need hundreds of products that aren't driving revenue." – Ryan Treft, Founder & Partner of Coalatree and Peejamas
Investing in solid SKU tracking systems can lead to reduced excess inventory, better cash flow, and happier customers. With carrying costs making up 30% of inventory expenses, improving SKU management with data-driven strategies can have a direct, positive impact on your profits. Start with the basics, use automation where it makes sense, and keep refining your methods based on what the data tells you.
FAQs
How can businesses identify the ideal SKU turnover rate for their industry?
To figure out the best SKU turnover rate for your business, start by looking at industry benchmarks, as these can differ widely by sector. For instance, retail businesses usually aim for turnover ratios between 2 and 4. However, industries handling perishable items often need much higher rates to avoid spoilage.
You’ll also need to adjust these benchmarks based on factors like demand fluctuations, seasonal trends, and how long your products can be stored. By regularly analysing your turnover rates alongside inventory data, you can make sure your stock levels match your business objectives and meet customer expectations.
How can I effectively manage and reduce dead stock in my inventory?
To tackle dead stock and keep it under control, start with regular inventory checks. These reviews make it easier to spot items that are slow to sell or have become obsolete. Once identified, you can take action by offering discounts, bundles, or special promotions to move the excess stock. Another option is to explore new sales channels that might attract different customers. If selling isn’t viable, donating unsold goods to charity not only clears storage space but also supports a meaningful cause.
Looking ahead, improving your demand forecasting and inventory management can help prevent dead stock from piling up again. Tools that offer precise sales predictions and automated alerts for reordering can help you strike the right balance - keeping shelves stocked without overdoing it.
How does AI enhance demand forecasting and inventory management for SKUs?
AI plays a crucial role in demand forecasting and inventory management by analysing historical sales data, seasonal trends, and supply chain factors through advanced machine learning algorithms. With this, businesses can make precise predictions about the demand for specific SKUs.
By spotting trends and identifying irregularities, AI helps prevent stockouts, avoid overstocking, and maintain optimal inventory levels. This leads to smarter resource allocation, healthier cash flow, and a more streamlined supply chain.


